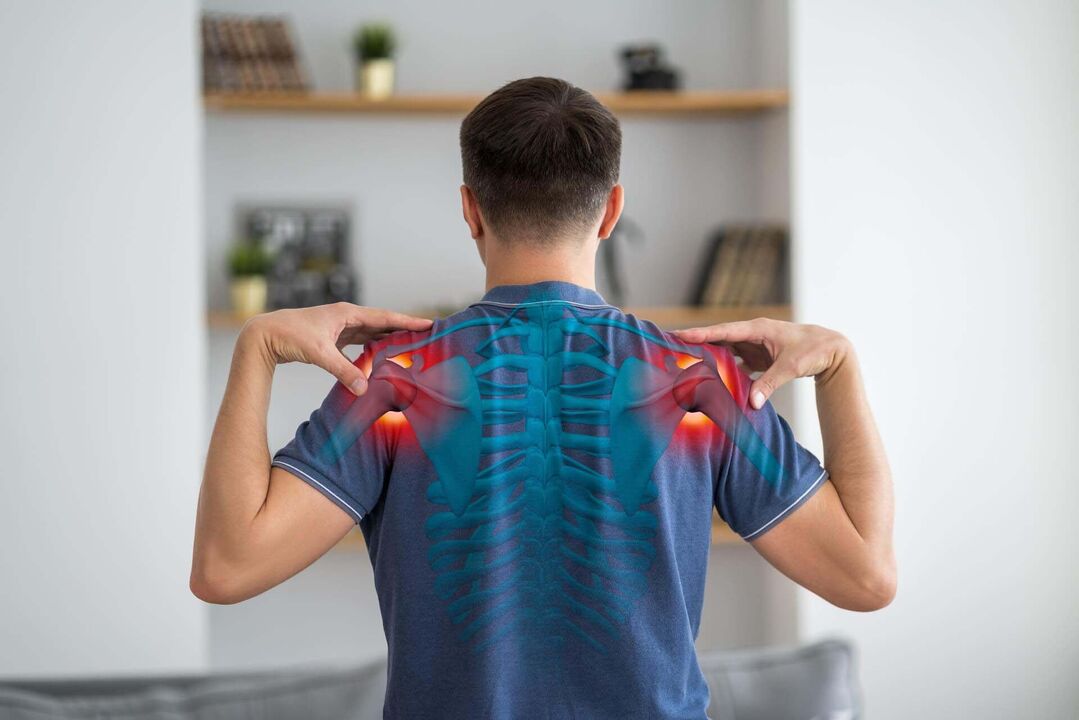
Osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is a dystrophic lesion of the cartilaginous plate that covers the articular surfaces of the joint, with subsequent involvement of the underlying bone.
About the disease
With this disease, not only the cartilaginous layer and subchondral bone are affected. The pathological process gradually also involves the joint capsule and ligamentous apparatus, the synovial membrane, the musculotendinous compartment and the subacromial region.
Osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint at a certain stage can lead to the development of osteoarthritis. This condition is characterized by the following symptoms: chronic pain, decreased range of motion in the joint, intra-articular crunching during rotation. Most often, people over 40 years old are subject to this transformation.
The main symptoms of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint are pain and limited mobility of the arm. To verify the diagnosis, imaging examination methods are informative: ultrasound and X-ray scanning, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
In accordance with clinical recommendations, the treatment of the disease in the initial stages is carried out using conservative methods, and in the later stages, when there is significant damage to the cartilage layer and the patient's self-care is impaired, it is joint replacement indicated.
Types of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
According to the classification, the following types of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint are distinguished:
- primary osteoarthritis, in the development of which genetics plays an important role, and even the most thorough examination does not allow us to identify the most important cause of the disease;
- secondary osteoarthritis, which is a consequence of the action of unfavorable factors in the joint (trauma, endocrine diseases, alteration of the anatomy of the joint).
Doctors judge the rate of progression of the pathological process by the degree of the disease. The more aggressive the process, the faster the destruction of the articular cartilage and the involvement of the underlying bone occurs. From a morphological point of view, there are 6 degrees of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint:
- first degree: the cartilage matrix swells and disintegrates, but the integrity of the superficial zone of the cartilage is not yet compromised;
- second degree: the cells of the cartilage tissue located in the deep layers are affected, the superficial cartilage plate is damaged;
- third degree - vertical cracks appear in the cartilage plate;
- fourth degree: the superficial zone of the cartilaginous plate gradually exfoliates, erosive defects form, and cystic cavities appear in the underlying bone;
- fifth degree: at this stage the underlying bone is exposed;
- sixth degree: the subchondral zone thickens significantly, the cysts become more pronounced, and marginal bone growths appear.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
The main clinical signs of shoulder osteoarthritis are pain, stiffness of the joint to the point of complete loss of mobility, as well as deformation of the joint.
The distinctive features of pain with deforming osteoarthritis are:
- appearance at the beginning of flexion, extension or rotation;
- increased during physical activity;
- nocturnal character due to stagnation of venous blood in the intraosseous canals;
- the presence of blockages - sudden jamming in the joint due to the separation of separate osteochondral fragments lying between the articular surfaces;
- Weather dependence: the pain intensifies when the weather changes (in humid and cold weather, the pain becomes more intense).
Osteoarthritis is a chronic pathology. At the initial stage of the disease, pain appears periodically (at the time of exacerbation of the disease). The rate of progression of the pathology is determined by the timing of initiation of treatment and the appropriateness of lifestyle modification. Shoulder pain becomes chronic if it persists for 6 months or more. The change from acute to chronic pain indicates the progression of the pathological process.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
The causes of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint are classified into 2 groups:
- modifiable – correction is possible;
- non-modifiable: it is not possible to influence its action.
Non-modifiable factors that may increase the risk of developing arthritic changes in the shoulder joint include:
- gender: up to 50 years old, women are less susceptible to the disease than men; after about 50 years, the prevalence of pathology among representatives of both sexes becomes approximately the same;
- the age of the person: the older the patient, the greater the risks (and from about 30 years old in the cartilage tissue, the degeneration process proceeds faster than the regeneration process, which creates the preconditions for the development of the disease);
- congenital anomalies of the shoulder structure: excessively increased mobility (hypermobility), dysplasia of connective tissue (normally, articular cartilage is represented by type 2 collagen fibers, with dysplasia, it is replaced by less durable types of collagen), instability of the joint;
- genetic characteristics: determined hereditary predominance of type 2 collagen, polymorphism of interleukin-1 and interleukin-2 genes.
Modifiable risk factors for deforming osteoarthritis of the right or left shoulder joint are:
- traumatic joint damage;
- excessive physical activity (strength sports and martial arts, including barbell bench press);
- Obesity - in shoulder osteoarthritis, the important factor is not the increased mechanical load, but the metabolic changes that occur in the connective tissue, incl. a state of chronic inflammation that accompanies obesity;
- weakness of the muscle corset of the shoulder joint, especially in those people who perform precise activities with their hands (jewelers, dentists, secretaries, writers);
- vitamin D deficiency, which is actively involved in maintaining the health of the musculoskeletal system;
- a diet low in vitamin C, which is an important link in the body's calcium and phosphorus metabolism;
- hormonal imbalance – thyroid disease, diabetes, etc. ;
- smoking, both active and passive.
In shoulder osteoarthritis, the main targets of the pathological process are the articular cartilage, the subchondral bone and the synovial membrane. In the affected cartilage, the synthesis of proteoglycans decreases, fragmentation and cracking of the plate is observed, exposing the underlying bone. The increase in non-physiological load on the bone causes its compaction, the appearance of cysts and osteophytes (marginal growths).
Diagnosis
Examination of a patient with pain in the shoulder joint should begin with x-rays. It is important to scan in several views to examine the joint in detail. Images can be taken in direct projection, in internal and external rotation positions. To evaluate soft tissue formations of the joint, especially in the early stage of osteoarthritis, ultrasound of the joint is the most informative. If the diagnosis remains unclear, an MRI/CT scan of the joint is recommended. In the next stage, the preservation of joint functions is evaluated.
Expert opinion
All morphological formations of the joint are involved in the pathological process. The main symptom of osteoarthritis is pain in the joint area, caused not only by synovitis, but also by bone damage (osteitis, periostitis), involvement of the periarticular soft tissues (tendonitis, tenosynovitis, myalgia, enthesopathies, stretching of the capsule articulate). , degeneration of the menisci and involvement of the neurosensory system (for example, irritation of the nerve trunks by large osteophytes). Therefore, the sooner you start treatment, incl. Modification of lifestyle, the more effective the control over the appearance of pain will be.
Treatment
At the initial stage of the pathological process, the treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is carried out by conservative methods, and with severe degeneration of the articular cartilage, surgical intervention (endoprosthesis) is indicated.
Conservative treatment
During the period of exacerbation of the process, the first priority is pain relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are most commonly used to relieve pain. They can be applied topically (in the form of creams and ointments), injected into the joint cavity, or used systemically (tablets, intramuscular injections). In some patients, the pain may be so severe that a short course of corticosteroids may be used to relieve it.
Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid or plasma, incl. Enriched with platelets, it can have a stimulating effect on the cartilage plate and promote its renewal (this treatment is considered pathogenic). These injections help accelerate the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers that form the basis of cartilage. As a result, the structure of the cartilage layer and synovial membrane improves, which helps to increase the congruence of the articular surfaces. These intra-articular injections help optimize the production of synovial fluid, which not only absorbs shock and hydrates the cartilage, but also improves metabolic processes in chondrocytes, increasing their internal potential.
Once the acute process has subsided, physiotherapeutic rehabilitation methods (pulsed currents, ultrasound and laser treatment) can be used as part of a complex treatment. These procedures have a complex positive effect on the joint structures.
Surgery
The operation is indicated in case of significant destruction of the cartilaginous plate, which is accompanied by persistent pain and dysfunction of the joint, leading to the inability to care for oneself and perform professional tasks. A modern method of surgical intervention for osteoarthritis of the shoulder is the implantation of an endoprosthesis. At SM-Clinic the operation is performed with strict adherence to the methodology using the latest generation endoprostheses. This is the key to achieving the best therapeutic results.
Prevention of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
Primary prevention of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint aims to maintain optimal metabolism in the osteochondral compartment. For this it is recommended:
- maintain a normal body weight;
- adequately compensate for endocrine disorders in the body (consultation and dynamic monitoring by an endocrinologist are required);
- dosed strengthen the muscular corset of the shoulder girdle;
- Warm up regularly if your professional activity involves performing similar movements on the shoulder.
To prevent the progression of developed shoulder osteoarthritis, the following recommendations are important:
- Avoid lifting heavy objects, incl. barbell push-ups;
- carry out repeated courses of therapeutic massage;
- regularly participate in gymnastics to improve health (under the supervision of a physiotherapy specialist).
Rehabilitation
After the stent, a cast is applied, which provides the necessary degree of immobilization. After the cast is removed, the period of restoration of the functional activity of the joint begins. For this, therapeutic massage, physiotherapy and gymnastics courses are recommended to improve health under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
Questions and answers
Which doctor treats osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint?
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by a traumatologist-orthopedist.
Representatives of which professions most often develop osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint?
Athletes who play volleyball, tennis, basketball, projectile throwers and loaders are at greatest risk of degenerative-dystrophic destruction of the cartilage layer of the shoulder joint.
Does shoulder pain indicate the development of osteoarthritis?
In fact, pain is the main sign of osteoarthritis. However, pain can also be a manifestation of other diseases: adhesive capsulitis, osteoarthritis, damage to the rotator cuff muscles, etc. A qualified orthopedic traumatologist will help you establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment.